Today, we are going to discuss a very common problem i.e., lumbago. Lumbago is a non-medical term that is used to describe low back pain. Lumbago is an extremely common ailment affecting the human race across the globe. 80-90% of human beings suffer from some kind of back pain in their lifetime.
LUMBAGO ICD 10- Diagnostic Code M54.5: Low back pain
Before we get into the prevention and treatment of low back pain, first have a look at the causes of it.
COMMON CAUSES OF LUMBAGO (80%)
- Poor posture: Improper posture attained during sitting, walking, standing, or doing any kind of activity places a huge amount of load on the back, This load on the back results in backache. This is the most common cause of low back pain.
- Occupational backache: Certain occupations like garbage collectors, porters, etc places enormous stress on the back resulting in lumbago.
- Obesity: Protruding belly places enormous strain on the back resulting in back pain.
- Muscle strain: In 80% of the cases, backache is due to the strain of the back muscles during activity, sports, trauma, etc.
- Prolapsed lumbar intervertebral disk: This is the second most common cause of low back pain. It occurs usually due to improper weight lifting.
- Facet joint osteoarthritis: Due to old age, repeated bending and twisting activities lead to arthritis of facet joints.
- Unaccustomed activities: A sedentary person suddenly adopts an active life.
UNCOMMON CAUSES OF LUMBAGO (20%)
- Congenital causes-
- Scoliosis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spina bifida
- Spondylolysis
- Infective conditions-
- Osteomyelitis
- Tuberculosis
- Brucellosis, etc.
- Traumatic causes-
- Vertebral body injuries, posterior arch fractures
- Muscle strain/sprain
- Prolapsed disk
- Inflammatory causes-
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosis spondylitis
- Metabolic causes-
- Osteoporosis
- Osteomalacia
- Degenerative conditions-
- Osteoarthritis
- Lumbar spondylosis
- Referred pain from-
- Gynecological diseases
- genitourinary diseases
- Gastrointestinal conditions, etc.
CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF THE BACK
- Inspection: With the patient in a standing position, look for postural abnormalities like scoliosis, lordosis, or kyphosis.
- To test flexion: Instruct the patient to bend forwards at the waist. (Normal flexion is 80 degrees or fingertips 3 to 4 inches from the floor).
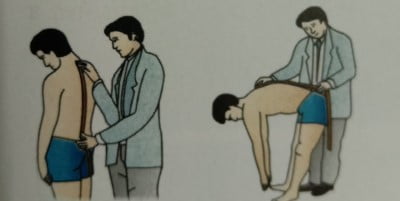
- Lateral flexion: Instruct the patient to bend to the left and the right as far as possible. (The normal range is 35 degrees on each side).
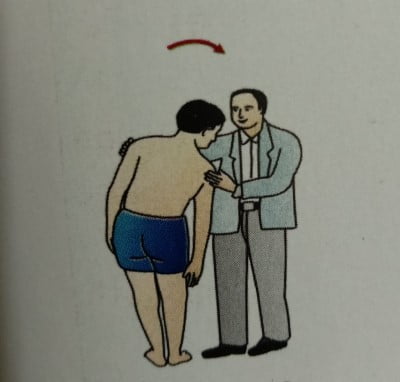
- Extension: Instruct the patient to bend at the waist as far as backward as possible. (The normal range is 20 to 30 degrees).
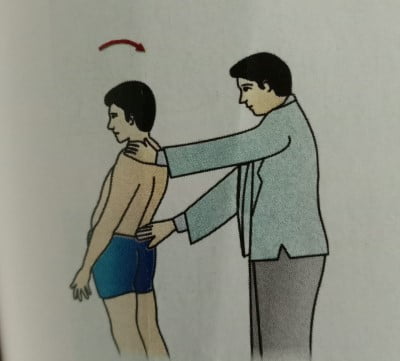
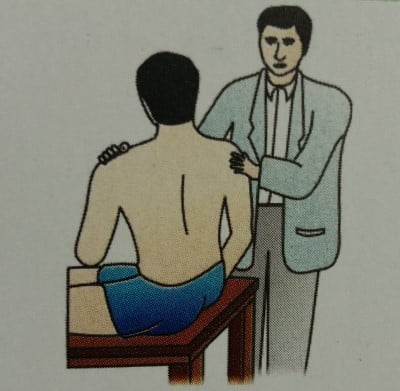
- Rotation: Tell the patient to rotate from the waist to the left as well to the right as far as possible. The normal range is 45 degrees per side).
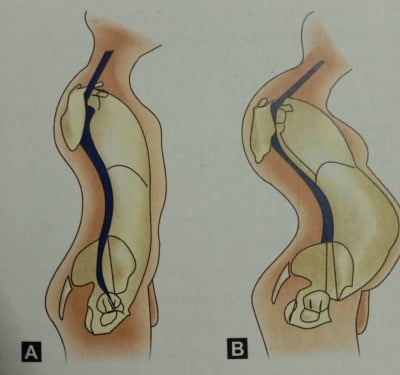
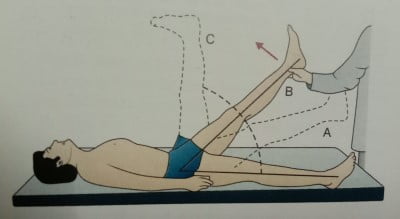
- SLRT: The patient should be in the supine position. Raise his leg to the point of pain. (A) Up to 30 degrees, the sciatic nerve is not under stretch. (B) 30-70 degrees, the nerve is stretched by prolapsed disk, hence positive. (C) Pin between 70-90 degrees, is not due to disk prolapse but due to sacroiliac joint arthritis.
READ MORE- Sciatica exercises and PT treatment
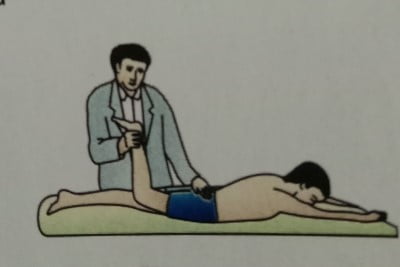
- Femoral nerve stretch test: Here the patient is in a prone position and is asked to lift the leg straight. The presence of pain in the anterior aspect of the thigh indicates a high nerve disk lesion (L 1-2-3)
PREVENTION OF LUMBAGO
Prevention of lumbago consists of-
- Proper postural habits/ Ergonomics
- Proper work environment
- Back exercises (will be discussed under the treatment part)
Proper Postural Habits
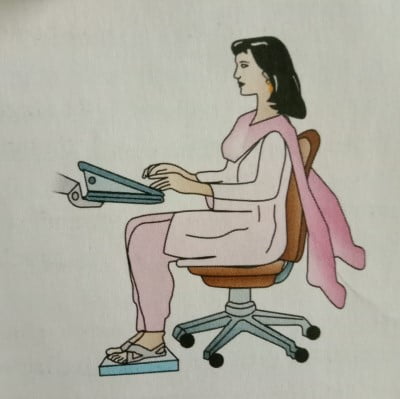
- PROPER WAY OF SITTING: Ensure your back is firmly touching the back of the chair. Keep the knees slightly higher than the hips. Sit close to your desk to avoid forward bending. Do not sit for too long. While driving, move the front seat close to the steering wheel and both hands should be kept on the wheel.
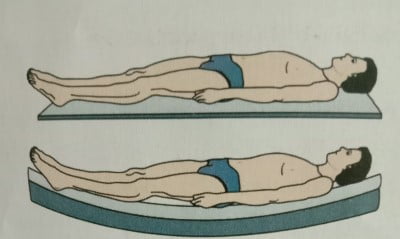
- CORRECT CHOICE OF MATTRESS: The mattresses should be firm to support the physiological curves of the back. If the mattress is too soft, the back will sag and if it is very hard will cause more pressure. Use a firm mattress, neither soft nor hard.
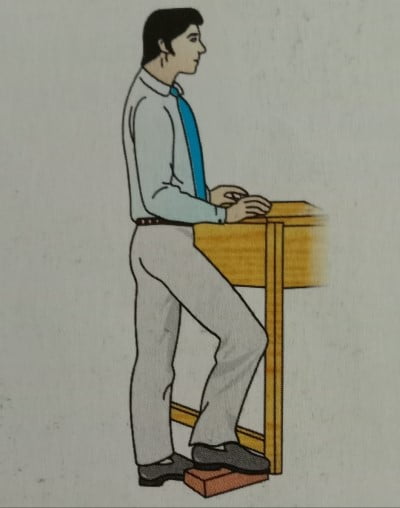
- CORRECT STANDING: Keep one foot in front and knees slightly bent while standing upright. If you have to stand for a long time, try keeping one foot higher than the other, on a low stool. Change your position often.
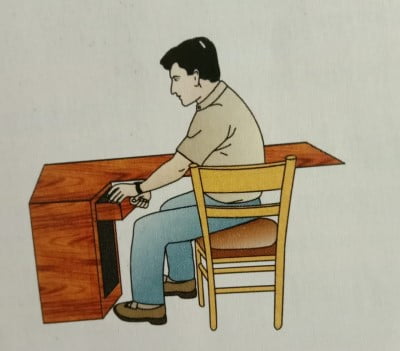
- CORRECT WAY OF TURNING: Do not twist your waist for turning or reaching out. Rather, turn by moving your feet. Keep the phone and such like objects within easy reach; don’t strain to reach them.
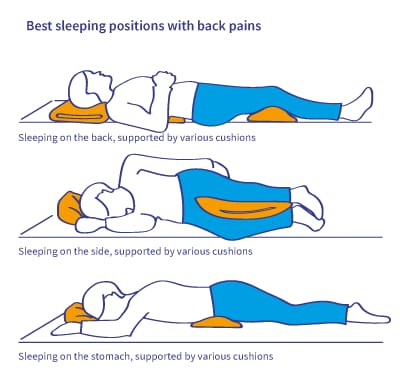
- CORRECT SLEEPING:
- If you sleep on your back: Prefer a thin pillow under your head. Add 1 or 2 pillows under your knees may help ease back pressure
- If you sleep sideways: Place a thick pillow to support your head and neck. Also, add a pillow between your knees to keep your spine in neutral alignment.
- If you sleep on your stomach: You should put your head on a very thin pillow or directly on the mattress. Place a thin pillow underneath your pelvis to keep your back in alignment. But sleeping on your stomach should be avoided as much as possible due to the risk of neck strain.
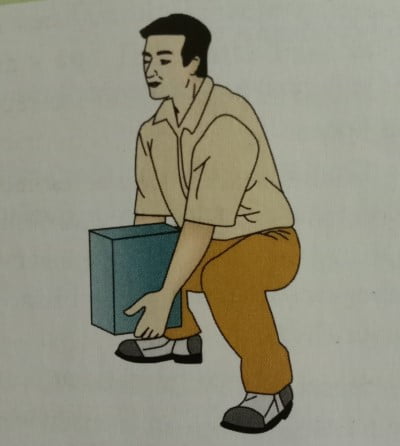
- CORRECT WAY OF LIFTING: Bend at your knees and not at your waist. Hold the object you are lifting close to your body and not higher than your chest. It is easier to push rather than pull heavy objects, e.g., furniture, and keep the knees bent while pushing.
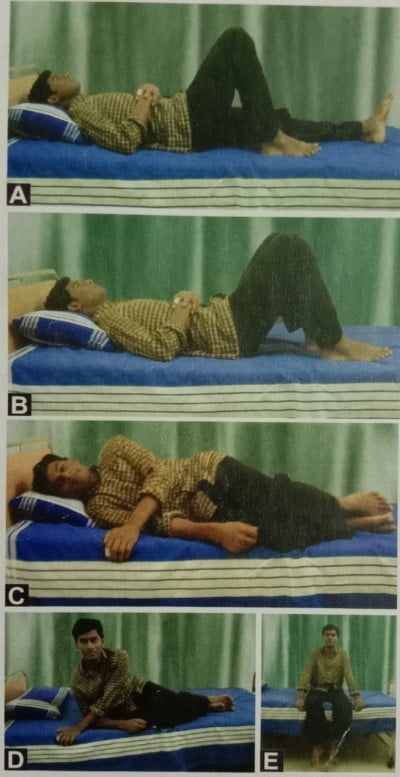
- CORRECT METHOD OF GETTING UP FROM BED:
- Bend your knee first
- Now bend the other knee
- Turn to the sides
- Pushing the bed with your hands get up,
- Sit on the edge of the bed for a few seconds.
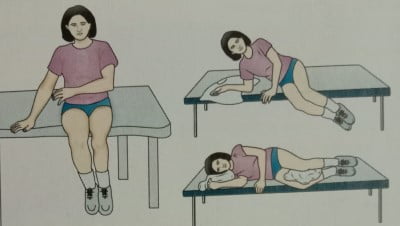
- CORRECT WAY OF RETIRING TO BED:
- Sit on the edge of your bed first
- Then lie down on your side
- Put the pillows according to your sleeping position as mentioned above.
Proper Work Habits
Use of proper chairs
Our backs were designed to walk on all four limbs and were not designed to sit. During evolution, the man adopted the two-legged stance and spent nearly 60% of their lifetime sitting. The pressure on the spine is least in the supine position, 3 times more on standing, and 11 times more during sitting. Thus, sitting is the most stressful on the back.
Most of the jobs involve sitting. One must adopt a proper posture and proper chair while sitting.
- Choice of a proper chair: A proper chair should maintain the physiologic S curve’ of the spine. Most of the chairs used in the office make the person assume a ‘C curve’ rather than the ‘S curve’. This places enormous stress on the back and leads to lumbago.
- Maintain a proper posture in the chair: Posture in the chair is extremely important and it is done as follows:
- The neck should be slightly forward and the upper back should be straight.
- Shoulders should be in a relaxed state and the arms should hang naturally.
- The back must be in full contact with the backrest of the chair.
- The angle behind the knee should be >90 degrees.
- Elbows and arms should rest on the arms of the chair.
- Thighs must be parallel to the floor and feet must be flat resting on the floor.


- Avoid sitting on the stools, crouching forwards on the table, and sitting with the legs on the top of the table.
- Health breaks: Taking a ‘health break’ while at work in the office at regular intervals is very important.
Ways of taking health breaks
- Take a short quick walk in the office at the end of one hour.
- Exercising the back and neck swiftly at the end of every hour.
- If there is no proper space to walk, then, in this case, a stepper can be helpful to taking a walk.
- Abrupt twisting, prolonged standing, improper sitting, etc should be avoided.
TREATMENT OF LUMBAGO
PRINCIPLES:
The principles of treating lumbago or lower back pain are explained by the 3 R.
- Relieve pain in acute cases
- Restore normal movements in chronic cases
- Recurrence is to be prevented
A patient who is suffering from back pain needs a multi-prolonged approach to successfully combat the causative factors and relieve the patient from pain. The various treatment options are:
- BED REST: The intradiscal pressure is lowest when the patient is supine. This is the rationale for the patients suffering from acute back pain.
- CRYOTHERAPY: It is indicated in acute cases of lumbago. It helps to reduce pain, swelling, and muscle spasm.
- THERMOTHERAPY: Heat causes vasodilation thereby reducing muscle ischemia.
- TENS: This is effective in relieving both acute and chronic pain.
- TRACTION: A traction is a form of treatment for lumbago that is followed for ages. Undoubtedly, it is one of the most popular methods of conservative management of lumbago.
- CORSET/BRACES: More than 99% of orthopaedists use corsets and braces to treat lumbago. It increases the intra-abdominal pressure and hence reduces the pain in the lumbar spine.
- SPINAL MANIPULATIONS: It is a skilled technique that is to be done by a trained person. It relieves pain by setting the right alignment of the spine.
- MASSAGE: Massage helps by stimulating the tissues and thus relaxes the contracted muscle.
- EXERCISES: Exercises reduce back pain by stretching the contracted muscles & strengthens the weak muscles. The exercises for lumbago could be flexion exercises, extension exercises, rotational exercises, and aerobic exercises. The choice of exercise whether flexion or extension should be made depending on the specific indications which will be discussed in the upcoming article.
- McKenzie’s APPROACH TO LOW BACK PAIN TREATMENT
READ MORE: Lumbago treatment in detail
CONCLUSION:
Today, we discussed a very common ailment i.e., lumbago. We have also seen the causes of it. Maintaining a proper posture while doing daily activities can be very beneficial in preventing back pain. If you are also suffering from back pain then you must look at your posture and your body ergonomics as bad posture is one of the commonest causes of lumbago.
ALL THE BEST!

