It is a common saying, “lifting heavy with fewer reps will make you bulky while lightweight with more reps will tone you up”. Is there really any difference between the two? Yes, there is. But it’s not like how you see it. It’s all about muscular strength and endurance.
Muscular strength and endurance
Muscular strength is the force, the muscle can exert against resistance. As you lift and lower weight, your muscle must generate enough force to move that weight. Determining the amount of weight that can be lifted in one repetition of exercise help to assess muscular strength. Strength and be developed by increasing the amount of weight that can be lifted in an exercise. For e.g., Doing 5-8 reps of bench press with a heavyweight.
Muscular endurance is the ability of muscles to apply force repeatedly. It can be described as how long or how many times you can lift or lower the weight. It can be assessed by determining the number of times a particular exercise can be performed. For e.g., doing 50 squats in a row.
If you are confused about whether you are working on your strength or endurance, have a look at the weight and the number of reps you are doing.
Fewer repetitions with heavyweight will help you increase your strength. More reps with less weight will build up endurance. Cardio exercises are also helpful in improving endurance.
READ MORE: Why is cardio important?
Benefits of muscular strength and endurance
Both muscular strength and endurance are important and you need both in daily life. There are a lot of benefits of strength and endurance training:
- Improve capabilities of performing physical work and activities of daily living.
- Help to fight depression and increase confidence by the way you look.
- Improve posture
- Helps in management of stress and anxiety
- Ease back and neck pain
- Relieve arthritis pain and improve range of motion
- Help control blood glucose level. Strong muscles are better at sopping up sugar in the blood and make body sensitive to insulin.
- Helps to prevent osteoporosis as strength training build bone stronger and slows bone loss.
- Prevent falls and fractures by maintaining balane of the body.
- Relieve some of the load carried by the heart and hence puts less strain on the heart.
- Increase metabolism even while resting and thus keep weight in a healthy range.
Developing different types of muscle fibers
Muscles consist of many muscle fibers. Two types of muscle fibers exist according to their contraction speed and energy source.
Type I slow-twitch fibers: They do not contract as rapidly or strongly as fast-twitch fibers. They are fatigue-resistant and rely on aerobic energy metabolism.
Type II fast-twitch fibers: They do contract quickly and forcefully, but fatigue more rapidly than slow-twitch fibers. They rely on anaerobic energy metabolism.
Endurance activities (e.g., jogging) build slow-twitch fibers. Power and strength activities (e.g., sprinting) build fast-twitch fibers.
Types of exercise for developing muscular strength and endurance
1) Isometric exercises:
Isometric (static) exercises contracts muscle without changing length. For e.g., planks. wall sit, calf raise hold, static lunge, etc.
Advantages:
- Require no or little equipment
- Low risk of muscle soreness
- Can be done in a small space
- Ra[pid strength improvement
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to devise a full-body workout
- Not very motivating
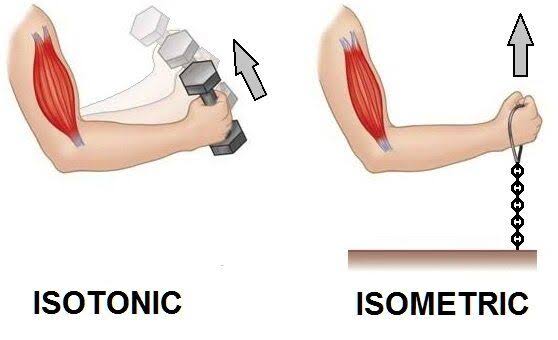
2) Isotonic exercises:
Isotonic (dynamic) exercises contracts muscle in a way that changes muscle length. Isotonic is the most popular type of exercise for increasing muscle strength. It can be performed with weight machines, free weights, or your own body (i.e., push-ups).
Advantages:
- Improve strength across entire range of motion
- Helps improve joint flexibility
- More motivating
Disadvantages:
- Require more exercise equipment
- High risk of muscle soreness
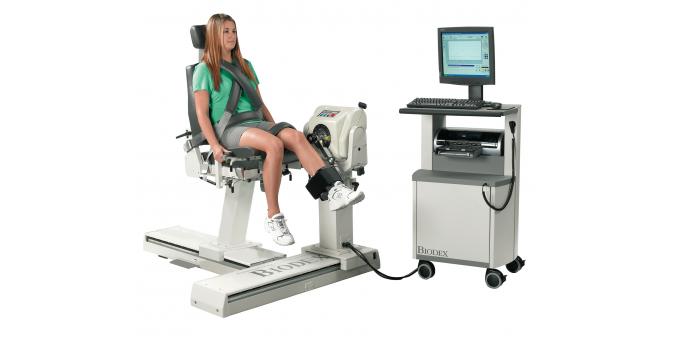
3) Isokinetic exercises:
In this, maximum tension is generated in the muscle as it contracts at a speed over the full ROM of the joint. Isokinetic exercises combine the advantages of both isometric and isotonic exercises. It uses special apparatus to provide maximum resistance to the muscles throughout the full range of motion. This equipment is often used by individuals during rehabilitation.
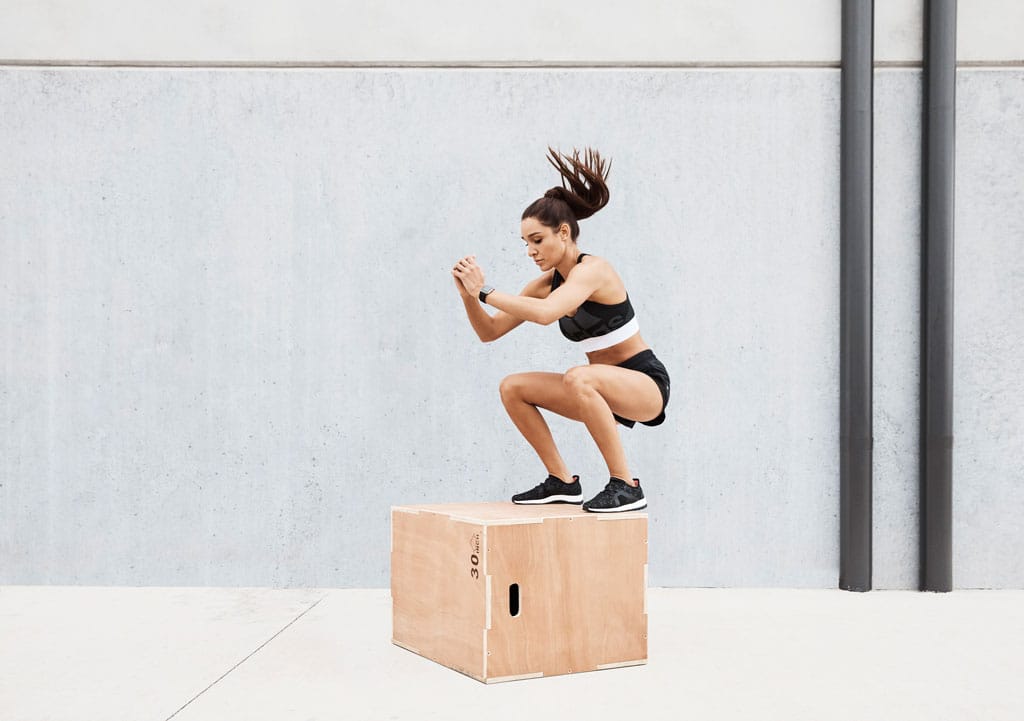
4) Plyometric exercises:
Plyometrics is a form of training where muscles are subjected to rapid alternation of lengthening and shortening while resistance is continuously applied. It involves doing abrupt, explosive movements, such as bounding on and off a box. It develops fast-twitched muscle fibers but risks incurring injury.

Exercise guidelines for muscular strength and endurance
For muscle strength: 3 to 5 sets of 3 to 8 reps, with a weight that cannot be lifted more than 8 times. Rest at least 120 seconds between sets.
For muscle endurance: 2 to 3 sets of 12 – 15 reps, with a weight that cannot be lifted more than 15 times. Rest 30 to 60 seconds between sets.
Conclusion:
Both muscular strength and endurance are equally important for doing daily life activities. Your exercise program should include activities that are helpful in improving strength as well as endurance.
ALL THE BEST!
