WHAT IS PLICA & WHAT IS PLICA SYNDROME?
The plica is a fold in the knee’s synovial membrane. The plica is the embryological remnant that may remain in some people after birth. It may be present in 20% to 50% of knees. It is a result of incomplete or partial reabsorption during fetal development. The plica can be inferior, medial, or superior to the patella and can also vary in length and thickness.
Plica syndrome or synovial plica syndrome can occur when the plica becomes irritated or inflamed usually following trauma. It can affect males and females in a similar manner, most commonly between 10-30 years of age. The majority of the plica are asymptomatic.
ICD-9-CM CODE: 727.83
ICD-10-CM CODE: M67.50
The etiology of the plica syndrome is unclear. But, potential causes of inflammation may include:
- Repetitive knee straightening and bending
- Blunt trauma of the knee
- Twisting of the knee
- Irritation of the knee fat pad
- Altered knee motion
- Loose bodies
- Meniscal tears
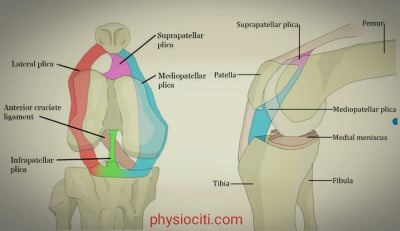
Anatomy of plica:
- MEDIAL PLICA: It extends from the anteromedial aspect of the patella to the suprapatellar pouch.
- SUPRAPATELLAR PLICA: It separates the suprapatellar pouch from the knee joint.
- INFRAPATELLAR PLICA: Also known as ligamentum mucosum. It extends from the infrapatellar fat pad to the intercondylar notch.
Signs & Symptoms of Plica Syndrome:
- Insidious onset of knee pain
- Pain in the anterior knee
- Sometimes catching, clicking, or giving away may also be present
- Symptoms aggravated by the flexed position of the knee and by transitioning between flexion and extension
- Pain in squatting and stairs climbing
- Swelling over plica
- Tenderness on palpating over the plica
Differential Diagnosis:
- Meniscal tear
- Septic arthritis
- Osteochondritis dissecans
- Prepatellar bursitis
- Infections
- Patellar subluxation and hypermobility
- Synovitis
- Patellar tendonitis
Means of Diagnosis:
- X-Rays are usually normal.
- MRI will be helpful to visualize increased fluid in the synovial plica
- Arthroscopy
Special Tests For Plica Syndrome:
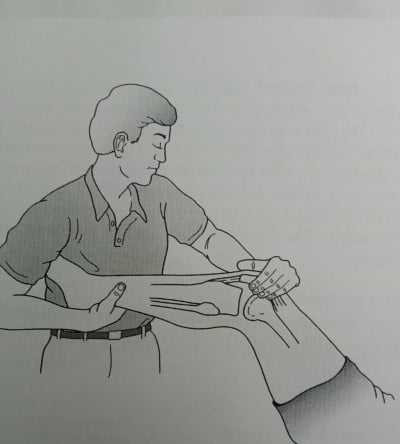
1) Hughston’s Test
For this test, the patient lies in the supine position. Then the examiner flexes the knee and rotates the tibia medially with one hand and presses the patella medially with the heel of the other hand. The fingers of the hand which is pressing the patella will palpate the medial femoral condyle.
The examiner will flex and extend the patient’s knee passively and will feel the popping of the plica band under the fingers. The popping will indicate a positive test.
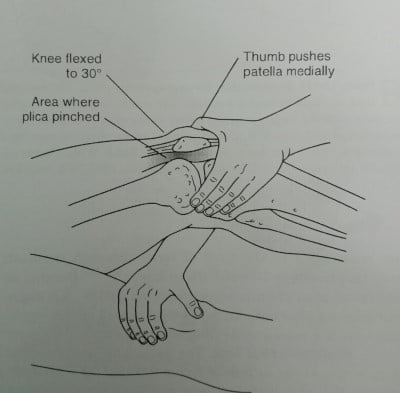
2) Mediopatellar Plica Syndrome Test
Also known as the Mital-Hayden test or Medial plica shelf test.
For this test, the patient lies in the supine position with the affected knee bend at 30 degrees. The bent knee should rest on a support or on the examiner’s arm. The examiner will then push the patella medially with his thumb.
If the patient complains of pain or a click, it will be a positive test. This pain or clicking will be due to the pinching of the edge of the plica between the patella and the medial condyle of the femur.
3) Patellar Bowstring Test
The patient will lie on his side with the affected leg uppermost. The examiner will push the patella medially with the heel of his hand and will hold the patella there. The examiner will then flex the knee of the patient and rotate the tibia medially with the other hand. After that, the patient’s knee will be extended and the examiner feels for any kind of sounds.
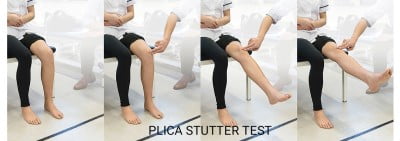
4) Plica “Stutter” Test
The patient will be in the sitting position on the edge of the table. Both the knees of the patient should be 90 degrees flexed.
The examiner then places a finger on one patella to palpate it during the movement. After that, the patient is asked to extend his knee slowly.
If the test is positive, then the patella will stutter or jumps somewhere between 60-45 degrees of flexion (0-degree being straight leg) during the movement. This test is effective only if there is no swelling.
Treatment of Plica Syndrome:
BY MEDICATIONS:
- NSAIDs (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Corticosteroid injection
- Antibiotics, if there is an infection
MEDICAL PROCEDURE:
- Arthroscopy if conservative treatment fails.
Intervention:
- Modification or avoidance of certain activities
- Immobilization of the knee in extension for a few days
- Avoid repetitive flexion and extension activities
- Avoid prolonged periods of knee flexion
- Modalities:
- TENS for pain control
- PRICE: Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
- Ultrasound
- Exercises
Exercises for plica syndrome usually involve strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and stretching exercises for the hamstrings.
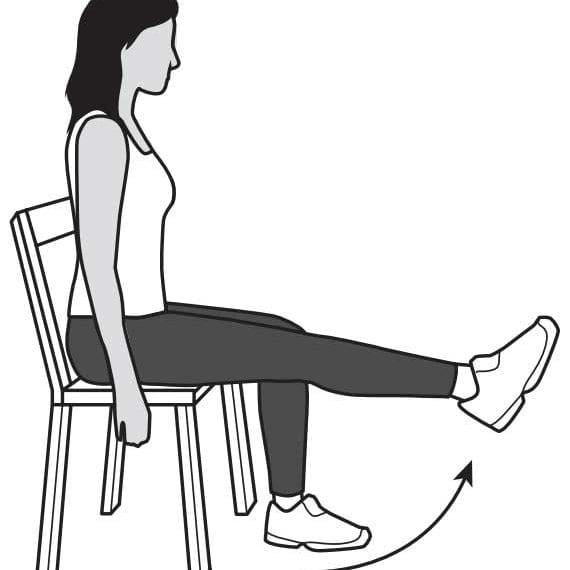
Quadriceps strengthening exercises:
- The patient sits on a chair and extends the knee as shown in the image below.
- Hold the straight knee for about 10-15 seconds and do it 10-15 times.
- The back should remain straight during the exercise.
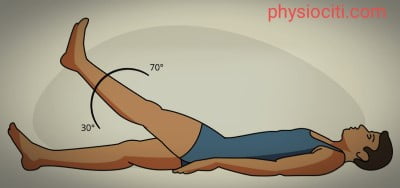
- The patient lies supine on a surface.
- Lift the leg up to 60 degrees as shown below with the knee straight.
- Hold the leg up for about 10 seconds.
- Repeat 10 times.
- For the goblet squats, hold the weight in front of your chest.
- Then squat down on a surface and keep your back straight and core tight.
- Try to keep your elbows between your knees as your squat down.
- Do 2-3 sets of 10-15 reps and progress gradually.

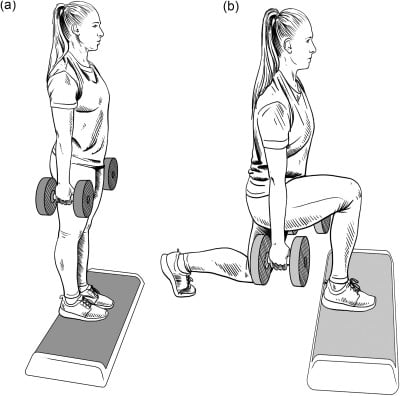
- Stand straight with dumbbells in both hands or without dumbbells with hands on your hips in beginning.
- Take a large step backward with one foot.
- Lower your hips until your other thigh becomes parallel to the ground.
- Knees should be maintained at 90 degrees as shown.
- Return to the starting position and then do it with the other leg.
- Do 2-3 sets of 10-15 reps.
Hamstring Stretching Exercises:
- Lie down in a supine position with both legs straight.
- Then take a towel or a band and wrap it around one foot.
- Try to straighten your leg with the help of a towel as shown below.
- You will feel a stretch on the back of your leg. Hold the stretch fo 10 seconds.
- Do it 10 times.


- In a standing position, extend one leg out on the floor as shown below.
- Keeping your back straight, bend at your hips and bring your chest towards your thigh.
- The other leg should bend slightly. Hold this position for 10-15 seconds.
- Repeat 5-10 times.

ALL THE BEST!
