Snapping scapula syndrome, another name for scapulothoracic crepitus, is a shoulder ailment that makes an audible popping or snapping sound when the movement of the arm. The sound is produced as the shoulder blade, or scapula, moves in opposition to the ribs. Snapping scapula syndrome is a common illness, although its precise etiology is unknown. We’ll examine the condition’s causes, signs, and available treatments in more detail in this post.
ICD-9-CM CODE- 726.10 Disorders of bursae and tendons in the shoulder region unspecified
ICD-10-CM CODE- Bursitis of unspecified shoulder
Causes of Snapping Scapula Syndrome:
Although the precise cause of snapping scapula syndrome is unknown, a number of factors seem to be present. Among the most typical causes are:
- Bony Abnormalities: A snapping sound can be produced by the scapula rubbing against the ribs due to bony irregularities, such as an uneven scapula shape.
- Muscle Imbalances:A snapping sound can result from abnormal movement of the scapula caused by abnormalities in the muscles around the shoulder.
- Joint Degeneration: Our joints may deteriorate with age, reducing our range of motion and stability. This may result in abnormal movement of the scapula and a snapping sound.
- Repetitive Movement: The scapula may move unnaturally during repetitive motions like lifting weights or tossing a ball, which can produce a snapping sound.
- Non-traumatic injury to the long thoracic nerve:
- Influenza
- Drug overdose
- Traumatic injury to the long thoracic nerve:
- Impact injury
- Stretch to the cervical spine
- Electrical shock
- Mastectomy with axillary node dissection
Symptoms of Snapping Scapula Syndrome:
A popping or snapping sound made by the moving arm is the primary sign of snapping scapula syndrome. Usually, this sound is accompanied by shoulder pain or discomfort. The following are additional signs of snapping scapula syndrome:
- Pain or Discomfort: Shoulder pain, which can vary in intensity from minor to severe.
- Stiffness: It is difficult to move the arm due to shoulder stiffness.
- Weakness: Arm weakness that makes it challenging to lift large objects.
- Decreased Range of Motion: reduced shoulder range of motion, which makes it challenging to reach overhead.
- Crepitus
- Muscle spasms along the rib cage
- Scapular instability
Differential Diagnosis:
- Scapular dyskinesis: a disorder wherein arm movements are not performed with the scapula moving smoothly and efficiently.
- Bursitis: Pain and discomfort are caused by inflammation of the bursae, which are tiny sacs filled with fluid that cushion the muscles and joints.
- Tendinitis: tendon inflammation, frequently brought on by overuse or repetitive motions.
- Fracture: a painful and uncomfortable break in one of the shoulder’s bones.
- Arthritis: joint inflammation that results in pain and discomfort.
- Pinched nerves: compression of a nerve that results in pain.
- Referred pain: Pain in the arm or shoulder that comes from somewhere else in the body.
Diagnosis:
Since the symptoms of snapping scapula syndrome are sometimes confused with those of other disorders, such as rotator cuff injuries or shoulder impingement syndrome, diagnosing the condition can be challenging. During a physical examination, a doctor would usually ask the patient to move their arm in various ways in order to assess whether or not there is any pain or discomfort. To obtain a better view of the scapula and surrounding structures, imaging procedures like MRIs and X-rays may be useful in some situations.
Treatment of Snapping Scapula Syndrome:
Physical therapy and exercises are commonly used in the treatment of snapping scapula syndrome in order to strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder, increase joint mobility, and address any muscular imbalances. Here are a few typical physical therapy exercises:
- Scapular Stabilization Exercises: To increase stability, the purpose of these exercises is to strengthen the muscles surrounding the scapula.
- Range of Motion Exercises: By increasing the shoulder’s range of motion, these workouts facilitate easier arm movement.
- Strengthening Exercises: By strengthening the arm and shoulder muscles, these exercises serve to increase general strength and lessen pain.
- If there is pain and inflammation, then
- Ice
- Rest
- Activity modification
- Ultrasound
- Electric stimulation
Surgery could be required in severe cases of snapping scapula syndrome in order to fix any underlying bone abnormalities or to replace any destroyed tissue. The precise source of the ailment and the degree of damage will determine the kind of surgery that is done. For cases of snapping scapula syndrome, typical surgical techniques include:
- Scapuloplasty: In order to decrease friction and increase mobility, the scapula is surgically reshaped during this treatment.
- Bursal Resection: Any bursae, which are tiny sacs packed with fluid, that are creating friction and adding to the snapping sound must be removed during this treatment.
- Tendon Repair: The snapping sound could occasionally be the result of injury to the tendons surrounding the shoulder. In order to lessen friction and increase movement, injured tendons are repaired during tendon repair surgery.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation will be required following surgery to aid in the shoulder’s healing and regained strength. It could take several months to finish and involve exercises to increase strength, stability, and range of motion.
Exercises for Snapping Scapula Syndrome:
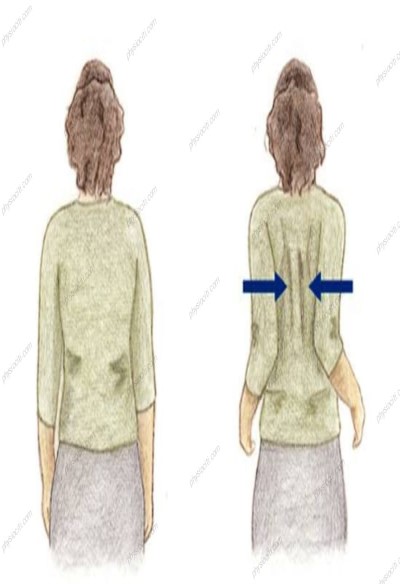
With your arms by your sides and your back straight, either sit or stand. Hold the scapula together for five seconds. Ten times over, repeat.
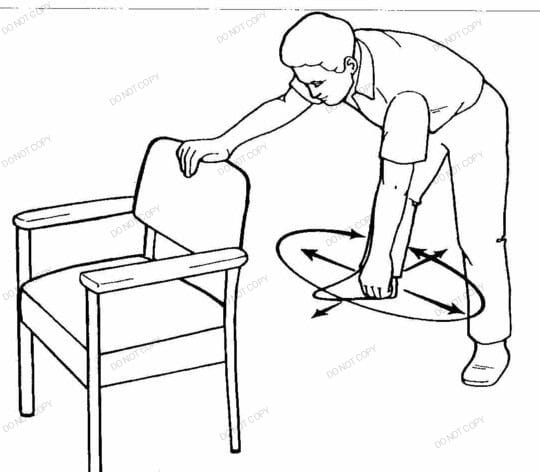
Bend your affected arm down and support your good arm on a table or chair while you stand. Make little circles with the affected arm, going in one way at first and then the other. As your shoulder heals, progressively enlarge the circles.
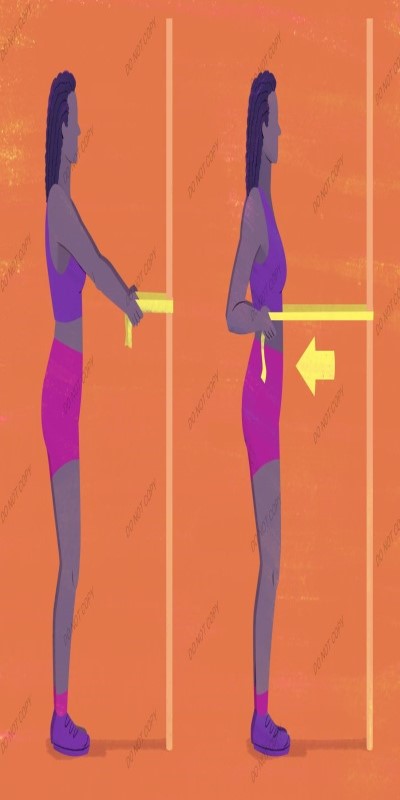
Hold a resistance band with your arms out in front of you while standing with your feet hip-width apart. Keeping your arms close to your sides, pull the band towards your chest. Ten to fifteen times, repeat.
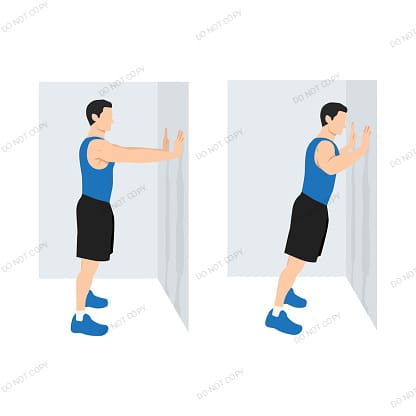


Put your hands shoulder-height on the wall while facing the wall with your back to it. Lower your body slowly toward the wall by bending your elbows, then push yourself back up to the starting position. Ten to fifteen times, repeat.
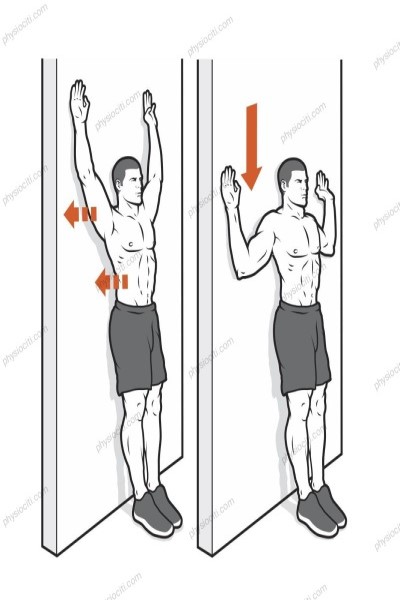
Place your arms over your head and lean your back against a wall. Sliding down the wall as far as you can while maintaining a straight arm position will return your arms to their initial position. Ten to fifteen times, repeat.
Maintain a hip-distance stance while gripping a set of dumbbells by your sides. Your shoulders should rise to your ears and then fall back down. Ten to fifteen times, repeat.
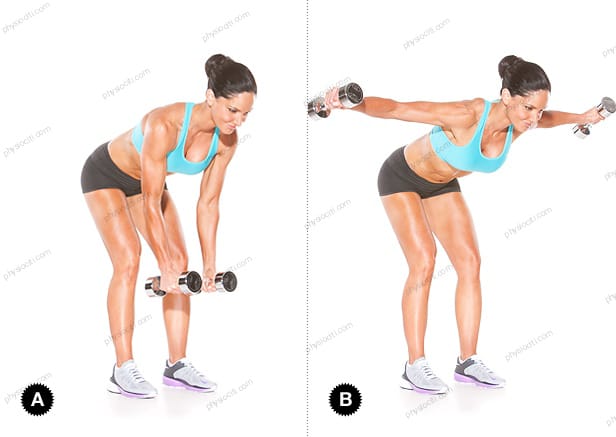

Keeping your feet hip-width apart, place two small weights in front of your thighs and stand there. Raise the dumbbells out to the sides until they are level with your shoulders, maintaining a straight arm position. Reduce them to their initial position. Repeat ten to fifteen times.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, the condition known as snapping scapula syndrome can result in a popping or snapping sound in the shoulder as the arm is moved. Although the precise etiology of this disorder is unknown, a number of factors, including anomalies of the bones, imbalances in the muscles, and deterioration of the joints, are thought to be involved. Physical therapy and exercises are commonly used in the treatment of snapping scapula syndrome in order to strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder, increase joint mobility, and address any muscular imbalances. In extreme circumstances, surgery might be required to fix any underlying abnormalities of the bones or to restore any destroyed tissues. Most patients with snapping scapula syndrome are able to heal and regain full use of their shoulder with the right diagnosis and care.
